Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Hashimoto, Makoto; Maeda, Koji; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1437 - 1446, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The aerodynamic radioactive median diameter (AMAD) is necessary information to assess the internal exposure. On June 6, 2017, at a plutonium handling facility in Oarai site of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), during the inspection work of a storage container that contains nuclear fuel materials, accidental contamination occurred and five workers inhaled radioactive materials including plutonium. Some smear papers and an air sampling filter were measured with the imaging plate, and we conservatively estimated minimum AMADs for two cases, plutonium nitrate and plutonium dioxide. As a result of AMAD estimation, even excluding a giant particle of a smear sample, the minimum AMADs of plutonium nitrate from smear papers were 4.3 - 11.3  m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1
m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1  m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0
m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0  m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9
m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9  m.
m.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobiyama, Mamoru*; Inami, Takashi*; Kambara, Tadashi*; Okuda, Shigeo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.171 - 175, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.85(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied effects of irradiation with energetic particles on defect accumulation in nanocrystalline gold (nano-Au). The specimens of nano-Au foil (3-5  m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV
m thickness) with various grain sizes (23-156 nm) are prepared by the gas deposition method and subsequent thermal annealings. Irradiations of the specimens with 60-MeV  C ions, 3.54-GeV
C ions, 3.54-GeV  Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production,
Xe ions or 2.0-MeV electrons are performed at low temperature. The defect accumulation behavior is observed by measuring the electrical resistivity change during irradiation. Through an analysis of defect accumulation behavior, cross-sections for defect production, 
 , and annihilation,
, and annihilation, 
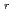 , in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E
, in nano-Au increase monotonically as the grain size decreases. These results are considered to be caused by the existence of a large volume fraction of the regions near grain boundaries in nano-Au where the threshold energy for atomic displacements, E , becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
, becomes lower than in polycrystalline gold. The possibility of electronic excitation effects in nano-Au is also discussed.
Takahashi, Satoshi*; Okuno, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
JAERI-Tech 2005-056, 51 Pages, 2005/09
In the heterogeneous system of the mixed oxide fuel of uranium and plutonium, hereafter, MOX fuel, it was investigated whether the system could be modeled as a homogeneous system on the conditions which dealt with the MOX fuel of particle diameter 0.02mm or less in MOX fuel fabrication facilities in Japan. The infinite multiplication factor of the homogeneous system of the MOX fuel was first calculated, and the optimum moderation condition over the each ratio of PuO was determined. It was verified that carried out critical calculation for the heterogeneous system of the MOX fuel in which the spherical fuel diameter in a cube unit cell increased, and an atomic number ratio of hydrogen to heavy metal fixed conditions, and the probability for neutrons to escape resonance by a spherical fuel diameter no less than 0.1mm, and analyzed critical conditions etc. using a contiguous energy Monte Carlo code MVPII and JENDL3.3. The details of these calculations are reported. These results are expected to be quoted in a revised edition of "Nuclear Criticality Safety Handbook."
was determined. It was verified that carried out critical calculation for the heterogeneous system of the MOX fuel in which the spherical fuel diameter in a cube unit cell increased, and an atomic number ratio of hydrogen to heavy metal fixed conditions, and the probability for neutrons to escape resonance by a spherical fuel diameter no less than 0.1mm, and analyzed critical conditions etc. using a contiguous energy Monte Carlo code MVPII and JENDL3.3. The details of these calculations are reported. These results are expected to be quoted in a revised edition of "Nuclear Criticality Safety Handbook."
Ishino, Masahiko; Yoda, Osamu; Haishi, Yasuyuki*; Arimoto, Fumiko*; Takeda, Mitsuhiro*; Watanabe, Seiichi*; Onuki, Somei*; Abe, Hiroaki
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 41(5A), p.3052 - 3056, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.92(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
JNC TN8400 2001-008, 36 Pages, 2001/03
Research on geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) has been underway in many countries. Bentonite exhibiting a low permeability, high swelling property and high sorption capacity for many radioelements is proposed as a buffer material in many countlies. Recently, cementitious materials are considered as candidate matelials for the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As the pH and the Ca, Na, K contents of hyperalkaline pore water from the cementitious materials are high, this hyperalkaline pore water would alter the buffer material. The main aim of this study is to investigate the effect of alkaline pore water into the bentonite. Used materials are montmorillonite, albite and quartz composing bentonite. These minerals mixed in a constant ratio (1:1wt%) made to react to distilled water and the alkali solutions (pH11-13). These studies have been conducted at temperatures of 50 - 150 C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test
C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test  Montmorillonite test
Montmorillonite test  Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E
Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E ) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
Oda, Yoshihiro; Funasaka, Hideyuki; Wang, X.*; Obara, Kenji*; Wada, Hitoshi*
JNC TY8400 2000-002, 47 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-064, 22 Pages, 1999/10
Four kinds of diffusion experiments; (1)through-diffusion(T-D) experiments for compaction direction dependency, (2)in-diffusion(I-D) experiments for composition dependency of silica sand in bentonite, (3)I-D experiments for initial bentonite gain size dependency, and (4)I-D experiments for the restoration property of an artificial single fracture in compacted bentonite, were carried out using tritiated water which is a non-sorbing nuclide to evaluate the effect of pore structural factors for eompacted bentonite on diffudion. For(1), effective diffusivities (De) in Na-bentonites, Kunigel-V1 and Kunipia-F were measured for 1.0 and 1.5 Mg m
m . For(2), apparent diffusivities (Da) in Kunigel-V1 were measured for 0.8, 1.4 and 1.8 Mg
. For(2), apparent diffusivities (Da) in Kunigel-V1 were measured for 0.8, 1.4 and 1.8 Mg m
m with silica sand of 30 and 50 wt%. For(3), Da values for 0.8, 1.4 and 1.8 Mg
with silica sand of 30 and 50 wt%. For(3), Da values for 0.8, 1.4 and 1.8 Mg m
m were measured for a granulated Na-bentonite, OT-9607 which grain-size distribution is in a rang between 0.1 and 5 mm. For (4), Da values in Kunigel-V1 which a single fracture was artificially reproduced and was immersed in distilled water for 7 or 28 days for the restoration of the fracture, were measured for 1.8 Mg
were measured for a granulated Na-bentonite, OT-9607 which grain-size distribution is in a rang between 0.1 and 5 mm. For (4), Da values in Kunigel-V1 which a single fracture was artificially reproduced and was immersed in distilled water for 7 or 28 days for the restoration of the fracture, were measured for 1.8 Mg m
m . Although De values in Kunigel-V1 were approximately the same for both compacted directions over the density, De values for perpendicular direction to compacted direction were higher than those for the same direction as compacted direction in Kunipia-F. For composition dependency of silica sand in bentonite, no significant effect of the mixure of silica sand in bentonite on Da was found. For initial bentonite grain size dependency, Da values obtained for OT-960 were approximately the same as those for Kunigel-V1 and no effect of initial grain size of bentonite on diffusion was found. For the restoration property of a single fracture in compacted bentonite, no restoration period dependency on Da was found. Based on this, it may be said that diffusion of nuclides in compacted bentonite, ...
. Although De values in Kunigel-V1 were approximately the same for both compacted directions over the density, De values for perpendicular direction to compacted direction were higher than those for the same direction as compacted direction in Kunipia-F. For composition dependency of silica sand in bentonite, no significant effect of the mixure of silica sand in bentonite on Da was found. For initial bentonite grain size dependency, Da values obtained for OT-960 were approximately the same as those for Kunigel-V1 and no effect of initial grain size of bentonite on diffusion was found. For the restoration property of a single fracture in compacted bentonite, no restoration period dependency on Da was found. Based on this, it may be said that diffusion of nuclides in compacted bentonite, ...
Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; ; *; *
Proc. of 7th Int. Conf. on Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Remediation (ICEM'99)(CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
; Yamaguchi, Akira
PNC TN9410 98-028, 33 Pages, 1997/12
The safety analysis of FBR plant system for sodium leak phenomena needs to evaluate the deposition of the aerosol particle to the components in the plant, the chemical reaction of aerosol to humidity in the air and the effect of the combustion heat through aerosol to the structural component. For this purpose, ABC-INTG (Aerosol Behavior in Containment-INTeGrated Version) code has been developed and used until now. This code calculates aerosol behavior in the gas area of uniform temperature and pressure by 1 cell-model. Later, however, more detailed calculation of aerosol behavior requires the installation of aerosol model into multi-cell thermal hydraulic analysis code AQUA. AQUA can calculate the carrier gas flow, temperature and the distribution of the aerosol spatial concentration. On the other hand, ABC-INTG can calculate the generation, deposition to the wall and flower, agglomeration of aerosol particle and figure out the distribution of the aerosol particle size. Thus, the combination of these two codes enables to deal with aerosol model coupling the distribution of the aerosol spatial concentration and that of the aerosol particle size. AQUA and ABC-INTG were developed separately, therefore, several subroutine were modified and composed. Especially, the interface program which exchanges data between these two codes is important to execute transient calculation. This report describes aerosol behavior model, how to install the aerosol model to AQUA and new subroutine equipped to the code. Furthermore, the test calculations of the simple structural model were executed by this code, appropriate results were obtained. Thus, this code has prospect to predict aerosol behavior by the introduction of coupling analysis with multi-dimensional gas thermo-dynamics for sodium combustion evaluation.
Tokuoka, Naochika*; Kobayashi, Mamoru*; Koyama, Takashi*
PNC TJ1636 96-001, 64 Pages, 1996/03
None
Tanaka, Tadao; K.Sriyotha*; Kamiyama, Hideo
JAERI-M 93-109, 16 Pages, 1993/05
no abstracts in English
Arai, Yasuo; *; Omichi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 202, p.70 - 78, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:91.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yamano, N.; Sugimoto, Jun; Maruyama, Yu; Soda, Kunihisa
NUREG/CP-0127, 0, p.271 - 281, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
 Co,
Co, Sr and
Sr and  Cs in a porous tuff; Mechanisms and kinetics
Cs in a porous tuff; Mechanisms and kineticsC.K.Park*; S.I.Woo*; Tanaka, Tadao; Kamiyama, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 29(12), p.1184 - 1193, 1992/12
no abstracts in English
Iwai, Takashi; ; Maeda, Atsushi; ; Handa, Nuneo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(5), p.455 - 467, 1992/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English